Comprehensive Treatment Options for Psoriasiform Dermatitis
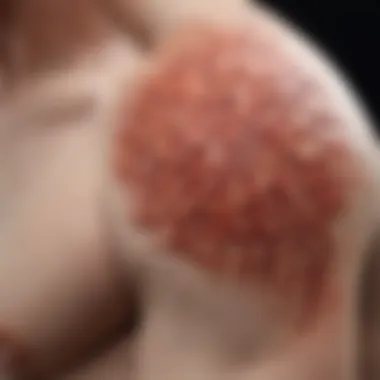

Intro
Psoriasiform dermatitis is a challenging condition that presents in ways often confusing to both patients and healthcare providers. While many may associate it primarily with psoriasis, the term encompasses a broader spectrum of disorders. Understanding this complexity is essential for effective treatment, emphasizing a multifaceted approach to management.
This article will explore various treatment strategies, focusing on both pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions. The aim is to provide clarity regarding the disease pathology, clinical manifestations, and appropriate diagnostic criteria. Through this exploration, we hope to offer insights that can aid in personalizing treatment plans, ultimately improving outcomes for individuals affected by this condition.
Research Highlights
Overview of Key Findings
Recent studies have shown that psoriasiform dermatitis can be effectively managed through a combination of treatments. These include topical therapies, systemic medications, and emerging biotechnological advancements.
- Topical therapies remain the first line in treating mild to moderate cases.
- Systemic treatments, including biologics, are crucial for severe and refractory cases.
- Non-pharmacological approaches, such as phototherapy and lifestyle modifications, provide additional support.
A significant finding is that individual responses to treatments can vary greatly, necessitating a tailored approach.
Significance of the Research
Recognizing and addressing the complexities of psoriasiform dermatitis is crucial. Misdiagnosis can lead to ineffective treatments and prolonged patient suffering. Research indicates a pressing need for updated clinical guidelines and training for healthcare professionals. This information not only optimizes treatment outcomes but also enhances patient quality of life.
"Understanding the intricacies of psoriasiform dermatitis allows for better-targeted therapies, ultimately reducing the burden on both patients and healthcare systems."
Original Research Articles
Summary of the Article
Studies investigating the efficacy of various treatment modalities have shed light on new approaches. A notable contribution is the assessment of innovative therapies that combine traditional pharmacological methods with novel technologies. Such research emphasizes the importance of ongoing education and adaptation in treatment protocols.
Author Contributions
Researchers from various backgrounds, including dermatology and pharmacology, have collaborated on this subject. Their diverse expertise enhances the depth of the findings and underscores the importance of a multidisciplinary approach in treating psoriasiform dermatitis.
Intro to Psoriasiform Dermatitis
Psoriasiform dermatitis is a complex condition that frequently presents challenges both in diagnosis and treatment. Understanding this dermatitis is crucial for effective management. This section will provide a comprehensive overview of psoriasiform dermatitis, diving into its definition, epidemiology, and clinical characteristics. These elements are essential for anyone involved in dermatological practice, research, or education.
Definition and Overview
Psoriasiform dermatitis is characterized by inflammation and scaling of the skin, often resembling psoriasis. The term highlights its similarity to psoriasis but does not always imply the same underlying etiology. This condition can manifest in various forms, making accurate classification vital for treatment.
In essence, the pathway to treatment starts with a clear definition. Misdiagnosis can lead to inappropriate treatment choices, underscoring the need for precise terminology and understanding. The recognition as a distinct entity calls for tailored approaches to management that may differ from those used for classic psoriasis.
Epidemiology
The prevalence of psoriasiform dermatitis varies across different populations. Research indicates that this condition affects both genders, although some studies suggest a slight male predominance in certain regions. Factors such as age and ethnicity can also influence incidence rates. Studies estimate that psoriasis and related conditions affect approximately 2-3% of the global population.
Environmental factors and genetic predispositions may also play roles in its occurrence. Increased awareness can lead to better identification and management approaches, allowing patients to receive the care they need.
Clinical Characteristics
Clinically, psoriasiform dermatitis presents with erythematous plaques, scales, and pruritis. It can spread in patches or lumps, and the severity may vary widely from mild to extensive coverage of the body. The lesions may develop symmetrically or asymmetrically and can be mildly resistant to conventional treatments.
A critical aspect of clinical assessment involves patient history, including previous treatments and family history of similar conditions. This understanding helps in differentiating psoriasiform dermatitis from other skin disorders such as eczema and seborrheic dermatitis, which may exhibit overlapping features.
Understanding these clinical characteristics is vital for effective treatment. A well-defined initial assessment can guide dermatologists toward successful management strategies that may significantly improve quality of life for affected individuals.
"A keen understanding of clinical characteristics can steer treatment plans toward successful outcomes."
With this foundation established, it becomes essential to explore the underlying pathophysiology of psoriasiform dermatitis in the subsequent section.
Pathophysiology of Psoriasiform Dermatitis
Understanding the pathophysiology of psoriasiform dermatitis is vital for comprehending the underlying mechanisms that drive this condition. This section explores the immune response, genetic predispositions, and environmental factors that contribute to its development. Recognizing these elements aids in formulating effective treatment strategies. By addressing the root causes, clinicians can optimize therapeutic interventions tailored to individual patients.
Immune System Involvement
The immune system plays a crucial role in psoriasiform dermatitis. Dysregulation of immune response leads to the overactivity of T cells, particularly T and T7 cells. These immune cells release pro-inflammatory cytokines, like interleukin 17 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha, which promote keratinocyte proliferation and inflammation. This abnormal immune activation results in the characteristic plaques and redness associated with the condition.
In clinical settings, targeting these pathways can significantly benefit patients. Treatments like biologics aim to inhibit specific cytokines involved in the inflammatory response, providing relief from symptoms and promoting skin healing. The relationship between the immune system and psoriasiform dermatitis underscores the complexity of managing the disease effectively.
Genetic Factors
Genetic predisposition is another critical aspect of psoriasiform dermatitis. Studies suggest that there is a familial component to the condition, with specific genes associated with susceptibility. The human leukocyte antigen (HLA) gene complex has been extensively studied. Variations in these genes can influence immune responses, making certain individuals more prone to developing the disease.
Identifying genetic markers can aid in prediction and early diagnosis. Furthermore, understanding the genetic basis of the condition opens new avenues for innovative therapies. Genetic research continues to evolve, shedding light on how these factors interplay with environmental triggers, potentially leading to personalized treatment plans for affected patients.


Environmental Triggers
Environmental factors significantly impact the onset and exacerbation of psoriasiform dermatitis. Common triggers include stress, infections, and skin injuries. Stress, for instance, can elevate cortisol levels, influencing the immune response and exacerbating symptoms. Similarly, certain skin infections can activate the immune system, leading to flare-ups.
Lifestyle choices also play a role. Poor dietary habits, alcohol consumption, and smoking may increase inflammation and worsen symptoms. Therefore, identifying and managing environmental triggers is essential. Patients who recognize these factors can modify their lifestyle, potentially reducing flare-ups and improving overall skin health.
"Understanding the interrelation of immune responses, genetics, and environment is essential for effective management of psoriasiform dermatitis."
In summary, the pathophysiology of psoriasiform dermatitis encompasses a complex interplay of immune dysfunction, genetic susceptibility, and environmental influences. A thorough understanding of these factors enables healthcare providers to develop comprehensive treatment strategies that address not just the symptoms but the underlying causes.
Diagnostic Evaluation
The process of diagnosing psoriasiform dermatitis is crucial due to its considerable implications on treatment options and patient outcomes. Understanding the nuances of diagnostic evaluation helps streamline the path towards effective management. An accurate diagnosis can be the difference between implementing a successful treatment regimen or exposing patients to unnecessary risks and ineffective therapies.
Clinical Assessment
Clinical assessment forms the foundation of diagnosing psoriasiform dermatitis. It involves a thorough patient history to understand the onset, duration, and characteristics of symptoms. Key elements include:
- Skin Examination: Observing the distribution and morphology of lesions is essential. Typical signs include erythematous plaques, scaling, and possible itchiness.
- Symptom Inquiry: Evaluating associated symptoms assists in understanding disease severity and impact on quality of life.
- Family History: Noting any familial predisposition can provide insights into genetic factors influencing the condition.
A complete clinical assessment may also involve scoring systems like the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) to quantify the severity for proper monitoring.
Histopathological Examination
Histopathological examination offers definitive information by studying skin biopsies under a microscope. This step is pivotal for distinguishing psoriasiform dermatitis from other skin conditions, such as eczema or cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Key findings in psoriasiform dermatitis often include:
- Acanthosis: Thickening of the epidermis caused by the overproduction of skin cells.
- Parakeratosis: Retention of nuclei in the stratum corneum, indicative of abnormal keratinization.
- Inflammatory Infiltrates: Presence of immune cells within the epidermis and dermis suggest active inflammation.
Such examination not only confirms the diagnosis but also helps in assessing the potential of the patient for response to various treatments.
Differential Diagnosis
Differential diagnosis is a necessary step to rule out other skin diseases that may mimic psoriasiform dermatitis. Conditions such as:
- Plaque Psoriasis: Often presents similarly but has distinct features and patient history.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: Differentiation can be made based on lesion locations and scaling characteristics.
- Lichen Planus: Requires careful evaluation of color, morphology, and associated symptoms.
Understanding these conditions allows for better-targeted approaches to treatment and aids in managing patient expectations.
Accurate diagnostic evaluation can significantly affect the effectiveness of therapeutic interventions and improve patient quality of life.
Pharmacological Treatments
Pharmacological treatments play a crucial role in managing psoriasiform dermatitis. These interventions aim to reduce inflammation, control symptoms, and improve the quality of life for patients. Medications can be categorized into topical therapies, systemic treatments, and phototherapy options. Each category has unique characteristics, benefits, and considerations that affect the choice of treatment.
Topical Therapies
Topical therapies are often the first line of treatment for localized cases of psoriasiform dermatitis. They are applied directly to the skin, providing targeted relief while minimizing systemic side effects.
Steroids
Steroids, particularly topical corticosteroids, are a common choice for treating psoriasiform dermatitis. They are known for their anti-inflammatory properties. Steroids work by suppressing the immune response in the skin, leading to reduced redness and itching. The popularity of steroids can be attributed to their rapid action and effectiveness in controlling flare-ups. However, prolonged use may result in skin thinning and other local side effects, necessitating careful management.
Vitamin Analogues
Vitamin D analogues are another effective treatment. These compounds, such as calcipotriene, can help regulate skin cell growth and differentiation. The key characteristic of vitamin D analogues is their ability to promote normal skin function while lowering inflammation. They are often used in combination with steroids to enhance therapeutic outcomes. A downside is the potential for irritation, which may limit their use in some patients.
Tazarotene
Tazarotene, a topical retinoid, is used primarily for its ability to normalize keratinization. This medication can prevent the buildup of skin cells that leads to plaques. Tazarotene is notable for its beneficial profile in treating moderate to severe cases. It is often preferred due to its efficacy in reducing psoriatic lesions without some of the adverse effects seen with steroids. However, patients may experience initial irritation, requiring gradual introduction to the treatment regimen.
Systemic Treatments
Systemic treatments are indicated when a patient's condition is more severe or widespread. These therapies affect the entire body and are often prescribed when topical treatments fail.
Methotrexate
Methotrexate is a cornerstone systemic treatment for psoriasis and psoriasiform dermatitis. It works by inhibiting specific immune system functions, which reduces inflammation. The key characteristic of methotrexate is its long-standing history of effectiveness in severe cases. It can significantly improve skin symptoms but may cause liver toxicity and other side effects, necessitating regular monitoring.
Cyclosporine
Cyclosporine is an immunosuppressant that can quickly control severe flares of psoriasiform dermatitis. It functions by inhibiting T-cell activity, thereby reducing inflammation. The benefit of cyclosporine lies in its rapid response, making it a valuable option in acute situations. However, its side effects include potential kidney damage and elevated blood pressure, which must be monitored during treatment.
Biologics
Biologics represent a more recent advancement in treatment, targeting specific pathways in the immune system. Medications such as adalimumab and ustekinumab are examples. The advantage of biologics is their targeted mechanism of action, which can lead to substantial improvements in severe psoriatic conditions. They do require regular administration and can lead to increased risk of infections, which is a consideration for patients.


Phototherapy Options
Phototherapy, or light therapy, is used as a complementary treatment option, often in conjunction with other therapies.
UVB Therapy
Ultraviolet B (UVB) therapy is a common form of phototherapy. It works by directly targeting the affected skin to reduce inflammation and slow down the growth of skin cells. A key characteristic is its safety and low side effect profile when administered correctly. Although effective, patients must adhere to a treatment schedule, and some may not achieve sufficient improvement with UVB alone.
PUVA Therapy
PUVA therapy combines psoralen (a drug) with UVA light exposure. This method is notably effective in treating severe cases that do not respond to other treatments. Its high efficacy makes it a good choice for difficult-to-treat areas. However, PUVA carries a risk of long-term skin damage, necessitating careful patient selection and monitoring.
Excimer Laser Therapy
Excimer laser therapy is a more targeted phototherapy that allows clinicians to apply laser light to specific skin lesions. The advantage of this method is that it helps to minimize damage to surrounding healthy skin. It is considered highly effective for localized lesions. However, the high cost and limited availability may restrict its use for some patients.
Non-Pharmacological Approaches
Non-pharmacological approaches are significant when managing psoriasiform dermatitis. These methods can complement medical treatments, providing holistic care. Addressing lifestyle and psychological wellbeing can lead to improved outcomes. Here, we consider two main categories: lifestyle modifications and complementary therapies. These have distinct roles but share a common goal of enhancing patient quality of life.
Lifestyle Modifications
Dietary Changes
Dietary changes are crucial for people with psoriasiform dermatitis. A balanced diet can have a positive impact on skin health. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish, are known for their anti-inflammatory properties. Foods rich in antioxidants, such as fruits and vegetables, can also support skin function. A key characteristic of dietary changes is their ability to reduce inflammation. This makes dietary adjustments a beneficial option for managing dermatitis. However, not all dietary changes work for everyone. Some individuals may notice little to no difference. It's important for patients to consult healthcare providers before making significant changes.
Stress Management
Stress management techniques can significantly contribute to controlling psoriasiform dermatitis. Stress is a known trigger for many skin conditions, including this one. Mindfulness and relaxation practices can lower stress levels. A focus on this topic highlights its key characteristic: the mind-skin connection. Effective stress management strategies can be beneficial choices for holistic treatment. Yet, some individuals may require more structured approaches, such as therapy or coaching, to manage their stress effectively.
Proper Skin Care
Proper skin care is fundamental to managing psoriasiform dermatitis. Regular moisturizing prevents skin dryness and can help relieve symptoms. A key characteristic of this practice is its direct impact on skin barrier function. Proper skin care routines often include products that are free from irritants and allergens. This makes them useful for those with sensitive skin. However, not all products are created equal. Some may aggravate symptoms rather than help. Careful selection of skin care products is essential for achieving the desired benefits.
Complementary Therapies
Acupuncture
Acupuncture serves as a complementary therapy for psoriasiform dermatitis. It is based on traditional Chinese medicine principles. This method aims to balance the body’s energy. Many find acupuncture beneficial for stress relief and reducing inflammation. The key characteristic of acupuncture is its non-invasive nature. For some individuals, it can offer a holistic approach to treatment. However, there is currently limited scientific evidence supporting its effectiveness directly on dermatitis.
Homeopathy
Homeopathy is another alternative often discussed regarding dermatitis. It involves using highly diluted substances to stimulate healing. Proponents suggest that it can help balance the body's responses. However, skepticism remains as many studies have failed to substantiate these claims. The key characteristic of homeopathy is its individualized treatment approach. While some may experience benefits, it may not work for everyone, thus presenting a unique mix of advantages and disadvantages.
Mindfulness Practices
Mindfulness practices can play an important role in managing stress related to psoriasiform dermatitis. Meditation and yoga are popular forms. These practices promote mental clarity and relaxation. A key characteristic is their focus on the present moment, which can minimize anxiety. Many find them beneficial in improving their overall emotional well-being. Yet, they require commitment and consistency for significant results. Not everyone may find these practices effective, indicating the need for personal exploration in choosing the methods that work best.
Emerging Treatment Modalities
Emerging treatment modalities represent a transformative element in the management of psoriasiform dermatitis. These innovative strategies offer hope for patients, particularly those who may not respond adequately to conventional therapies. As our understanding of the condition deepens, the need for effective and personalized treatment options has never been more pressing. In this context, emerging modalities include new biologics and gene therapy approaches.
New Biologics
New biologics are redefining treatment for psoriasiform dermatitis. These medications target specific components of the immune system. They work by inhibiting inflammatory pathways that are pivotal in the development of skin lesions. The advent of biologic therapy marks a significant shift from traditional systemic treatments, which often have broader effects and associated side effects.
Benefits of New Biologics:
- Targeted Action: They focus on particular targets like cytokines, reducing the breadth of side effects.
- Higher Efficacy: Clinical trials have shown that many new biologics outperform older therapies in terms of skin clearance and improvement in quality of life.
- Long-term Management: Patients may experience longer periods of remission, allowing for a more stable lifestyle.
In assessments, new biologics like Guselkumab and Risankizumab have shown promising results. Patient outcomes and feedback suggest a growing confidence in these treatments.
Gene Therapy Approaches
Gene therapy approaches present groundbreaking potential for treating psoriasiform dermatitis. This method aims to address the underlying genetic causes of the condition by modifying genes that play roles in inflammation and skin cell growth. Though still in early stages, gene therapy is becoming a focal point of research.
Considerations for Gene Therapy:
- Personalized Treatment: This therapy can be tailored to individual genetic profiles, improving efficacy.
- Long-lasting Effects: By altering gene expression, the treatment may offer more permanent solutions to management.
- Research Challenges: There are still many hurdles to overcome, such as delivery methods and ensuring patient safety.
Overall, the emerging treatment modalities in psoriasiform dermatitis bring optimism and dynamic strategies into play. Combining new biologics with developing gene therapies may empower patients, providing more effective and targeted options for management and care.
Long-term Management of Psoriasiform Dermatitis
Managing psoriasiform dermatitis requires a long-term strategy to ensure patient health and comfort. This chronic condition can have variable presentations, and its management often necessitates ongoing adaptation. Practitioners must consider not just the physical symptoms but also the psychological impacts, as long-term skin conditions can affect mental health. Regular management is crucial to minimize flare-ups, improve quality of life, and reduce the associated risks of co-existing conditions.


Monitoring and Follow-up
Regular monitoring and follow-up are essential to the effective management of psoriasiform dermatitis. This ensures that the treatment plans are effective and allows for timely adjustments as necessary.
Key elements to monitor include:
- Symptom severity: Regular assessment helps to track the progression of symptoms. A pain scale can be useful to quantify discomfort.
- Treatment effectiveness: Keeping a journal of treatment results enables both patient and provider to determine which therapies yield the best results.
- Potential side effects: Some treatments can lead to adverse effects that need to be managed. Regular check-ins help identify these early.
- Skin condition: Visual assessments and dermatological evaluations are necessary to ensure the skin is responding adequately to therapies.
Patients are encouraged to maintain open communication with their healthcare providers. Consistent visits allow for a mutual understanding of the patient's experiences and the effectiveness of the current treatment regimen.
Adjusting Treatment Plans
Adjustment of treatment plans is a critical aspect of long-term management. The response to treatment can vary among patients due to unique physiological factors or external variables.
Considerations for adjusting treatment plans include:
- Progression of symptoms: If there is no improvement or symptoms worsen, alternatives may need to be explored.
- New research: Emerging therapies may offer new solutions that are more effective than existing ones.
- Patient compliance: Sometimes, patients may struggle with medication regimens. Understanding these challenges and finding simpler alternatives may improve adherence.
- Environmental factors: Changes in environment or lifestyle can impact dermatitis. Treatment might need alteration due to these changing conditions.
Adjustments can involve increasing or decreasing medication doses, switching medications, or incorporating new non-pharmacological therapies such as dietary adjustments.
Through these continuous processes of monitoring and adjustment, practitioners can provide a more personalized treatment plan aimed at improving the patient's long-term prognosis and well-being.
Case Studies and Clinical Experiences
The exploration of case studies and clinical experiences is essential when discussing treatment for psoriasiform dermatitis. This section sheds light on real-world applications of various therapeutic approaches, offering insights that purely theoretical discussions may overlook. Clinical experiences often reveal the effectiveness of treatments in diverse populations and conditions, addressing the variability in patient responses.
In practice, successful outcomes from specific treatments can inspire both patients and healthcare professionals. For instance, documenting individual cases allows practitioners to learn from trial and error, refining treatment protocols tailored to the unique needs of patients. These narratives also provide invaluable evidence to support emerging therapies or modify existing regimens based on patient-specific factors.
Ultimately, case studies emphasize the importance of personalized treatment. Effectiveness often varies significantly across patients. Therefore, understanding these experiences can lead to better patient education and reassurance about potential outcomes.
Successful Treatment Journeys
Successful treatment journeys offer rich insights into effective strategies for managing psoriasiform dermatitis. An individual case might begin with a thorough assessment, identifying both physiological and psychological factors that contribute to the condition. For example, a patient may start with topical steroids alongside lifestyle modifications such as dietary changes and stress management techniques.
One noteworthy case involved a 35-year-old male who experienced severe skin lesions contributing to emotional distress. After an initial misdiagnosis, he started a tailored treatment combining methotrexate and mindfulness practices. Over the course of six months, careful monitoring and adjustments led to significant improvement in both skin condition and overall well-being. Furthermore, documented results show a lasting remission even after reducing treatment frequency.
Key Takeaways:
- Assessment of both physical and emotional factors is crucial.
- A combination of pharmacological and non-pharmacological strategies often yields better outcomes.
- Continuous adjustments to treatment plans based on patient response are necessary for sustained success.
Challenges and Strategies
Challenges in treating psoriasiform dermatitis are not uncommon. Skin conditions often involve a complex interplay of genetics, environment, and lifestyle choices. Patients may struggle with adherence to treatment or might experience side effects that lead them to discontinue therapy. Additionally, relapses during the maintenance phase can evoke frustration and anxiety for both patients and clinicians.
One case highlighted the trouble faced by a 45-year-old female with persistent lesions despite following a comprehensive treatment plan. Ultimately, the solution was found in a multi-disciplinary approach, integrating dermatological care with nutritional counseling and psychological support. This holistic strategy significantly improved her treatment experience and outcomes.
Strategies to Address Challenges:
- Education: Increasing patient knowledge about their condition and the importance of adherence improves compliance.
- Support: Providing psychological support to manage stress can enhance the overall effectiveness of treatment.
- Flexibility: Being open to alternative therapies when standard treatments fail helps maintain patient motivation and engagement.
Clinical experience and documented case studies are fundamental to evolving strategies in managing psoriasiform dermatitis. They offer a nuanced understanding that is critical for tailoring approaches to individual patient needs.
The End and Future Directions
The discussion of psoriasiform dermatitis does not end with the existing treatment options. This section underscores the importance of understanding both the current therapeutic landscape and the future directions that treatment may take. Effective management of psoriasiform dermatitis requires ongoing adaptation as new research emerges and therapies are developed. This dynamic nature of treatment underscores the necessity for healthcare providers to remain informed and agile in their approaches.
Summary of Treatment Options
Our exploration into psoriasiform dermatitis has revealed a diverse array of treatment modalities. From topical therapies like steroids and vitamin D analogues to systemic treatments such as methotrexate and cyclosporine, each option has its unique profile. Moreover, the potential of new biologics and gene therapies offers hope for more targeted treatments in the future.
- Topical Treatments: Effective for mild to moderate cases, these include steroids, which reduce inflammation, and newer agents like tazarotene, which promotes skin cell turnover.
- Systemic Treatments: Reserved for more severe cases, options such as methotrexate and biologics target underlying immune dysregulation.
- Phototherapy: Involves controlled exposure to UV light and can be particularly beneficial for patients unresponsive to other treatments.
Understanding the strengths and limitations of each therapeutic approach is vital for personalized patient care.
Importance of Personalized Medicine
Personalized medicine is a critical concept in the treatment of psoriasiform dermatitis. The response to treatment can vary widely among individuals due to genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. As a result, what works for one patient may not be as effective for another. By focusing on personalized treatment plans, healthcare providers can optimize treatment efficacy and minimize adverse effects. Tailoring therapy involves considering:
- Genetic predispositions that may affect drug metabolism.
- Existing comorbidities that may complicate treatment outcomes.
- Patient lifestyle and preferences, which can impact adherence to treatment regimens.
Incorporating these factors and utilizing biomarkers may lead to better-targeted therapies, improving overall treatment satisfaction.
Call for Continued Research
The landscape of psoriasiform dermatitis treatment is ever-evolving, making continued research imperative. Despite advances, many questions remain unanswered. Areas warranting further investigation include:
- Long-term efficacy and safety of emerging biologics and systemic treatments.
- Mechanistic studies to clarify the pathophysiological processes behind different patient presentations.
- Explorations into the influence of diet and lifestyle on disease progression and treatment response.
Investing in research not only enhances our understanding but also propels the development of innovative therapies, ultimately benefiting patients and clinicians alike.
"Continuous investigation and adaptability is crucial to advancing treatment protocols and improving patient outcomes in psoriasiform dermatitis."
This constant striving for knowledge reflects the commitment of the medical community to provide the highest standard of care to those affected by psoriasiform dermatitis.







